Our Services

AIR BALANCING
Using the appropriate instrumentation devices, air flow is measured and adjusted as per engineering specifications. Air balancing is important because it distributes air evenly across spaces. This can maximize both comfort, and efficiency.

HYDRONIC TESTING & BALANCING
Measuring and adjusting the flow rate to design criteria. This can also verify correct function of the associated pumps. This is important to ensure that equipment is getting enough flow to function properly. Equipment can include heat pumps, fan coil units, radiant heating, chilled beams, and heating & cooling coils.

AIR CHANGES TESTING
Testing air changes in various spaces to ensure adequate ventilation. This is a measure of the amount of times the air in a given space is completely replaced with clean air. The air change rate can be cross-referenced with recommended standards. A higher air change rate helps dilute air pollutants, and improves indoor air quality.

Fume Hood Testing
Testing and balancing fume hoods in laboratory spaces to ensure adequate ventilation and face velocity. Proper functioning of fume hoods is essential to the safety of the technicians, and the performance of the laboratory. Proper balancing of these systems will ensure that the fume hood alarm will not engage, preventing unnecessary down time.

Ultrasonic Flow Reading
Using a flow meter to determine the flow rate of a liquid through a pipe. This is useful in circumstance where circuit balancing valves, or other flow measuring devices are not available. It is possible to measure the flow rate through the pipe, to ensure that the related hydronic systems are functioning properly.
Sound Testing
Using a meter to measure acoustics at various bandwidths to determine the noise criteria. This data can then be cross-referenced with the recommended standards of the tested spaces. Various adjustments can be made, if necessary, to reduce noise in areas of concern.

Air & Hydronic Audits
Testing all air or water flows in a building to check for proper functionality. An audit is useful to provide insight on the overall functioning of a system. It is a useful indication of potential problem areas, where there is low flow. An audit will pin-point the location of a blockage, such as a closed fire damper, balancing damper, seized actuator or dirty strainer.
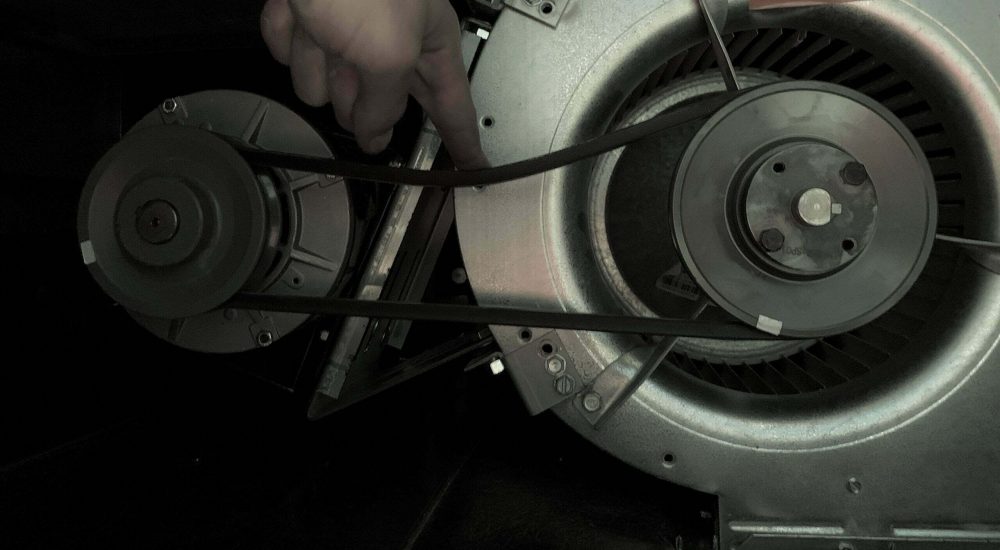

Sheave Changes
Changing motor and fan pulleys, as well as belts, in order to increase, or reduce supply or exhaust air. This is practical in situations where air flow needs to be increased without a costly replacement of the supply or exhaust fan. This can also be useful in a situation where noise levels need to be reduced.

CO / CO2 Testing
Engaging CO or CO2 sensors to ensure proper functionality of associated exhaust fans. This is done by safely replicating a real scenario of unsafe carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide levels. This tests the sensors ability to engage an alarm, and an associated interlocked exhaust fan.

Duct Leakage Testing
Duct Leakage Testing is an important diagnostic tool used to measure the efficacy of the installed duct work. Leakage in the ducts can reduce efficiency of the designed system. Thus, it is worth while to assess leakage within duct work systems, and seal accordingly.

HVAC System Mapping
As renovations occur over time, the HVAC layout of the building changes. Recreating the layout is useful for building managers, and building operators. It is also more organized to have complete sets of the entire HVAC system for maintenance purposes. We are able to map out and create professional Autocad and PDF drawings. These drawings of the actual on-site HVAC layout and are color coordinated and labeled for convenience purposes.
